How to Choose the Right Financial Instrument
Financial instruments are basically contracts that create financial assets for one party and liabilities for another. They come in various forms, including stocks, bonds, and derivatives. Each type of financial instrument serves a specific purpose and carries its own level of risk and reward. Understanding these can help you make informed choices. The actual Interesting Info about financial instruments.
What Are Financial Instruments?
Financial instruments can be thought of as the tools that facilitate the buying, selling, and management of financial assets. They are the building blocks of our economic system, enabling businesses to raise capital, governments to finance debt, and individuals to invest their savings. Understanding their structure and purpose is the first step in using them effectively.
The Role of Financial Instruments in the Economy
Financial instruments play a critical role in the global economy by providing mechanisms for risk sharing, capital allocation, and liquidity. They help allocate resources efficiently by directing funds to where they are needed most. This process not only supports economic growth but also stabilizes financial markets by providing transparency and risk management tools.
The Evolution of Financial Instruments
Over the years, financial instruments have evolved significantly, from simple promissory notes to complex derivatives. This evolution reflects changes in technology, regulation, and market demand. Understanding this historical context can give you insights into current market trends and future developments, aiding in more informed decision-making.
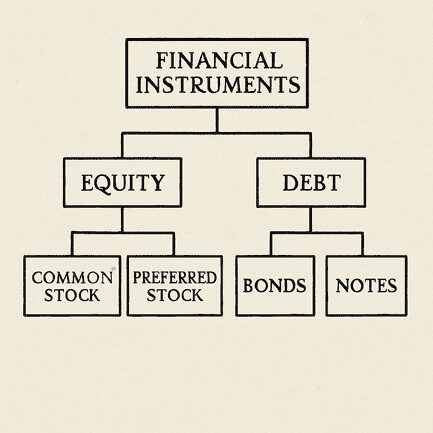
Types of Financial Instruments
Financial instruments can be categorized into several types, each with unique characteristics and uses. Here, we’ll explore some of the most common types and how they can fit into your investment strategy.
Stocks: Ownership and Growth Potential
- Understanding Stocks: Owning stocks means you have a share in a company. This ownership allows you to benefit from the company’s success and growth. Stocks can appreciate in value, providing capital gains, and may also pay dividends, offering a regular income stream.
- Risks and Rewards: While stocks can offer high returns, they come with risks, including market volatility and company-specific issues. Understanding these risks is essential for managing your investment portfolio effectively.
- Strategies for Investing in Stocks: Different strategies, such as value investing, growth investing, or dividend investing, can be used to tailor your stock investments according to your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Bonds: Stability and Income
- What Are Bonds?: Bonds are essentially loans you provide to governments or corporations. They promise to pay you back with interest over a set period. This makes them a relatively stable investment option, appealing to those seeking regular income.
- Types of Bonds: Bonds come in various forms, such as government bonds, municipal bonds, and corporate bonds. Each type has its own risk profile and return potential, influenced by factors like issuer creditworthiness and interest rate changes.
- Bond Investment Strategies: Successful bond investing often involves understanding interest rate trends and credit risk, as well as diversifying across different types of bonds to mitigate risk.
Mutual Funds: Diversification Made Easy
- How Mutual Funds Work: Mutual funds pool money from many investors to buy a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. This allows individual investors to access a broader range of investments than they could on their own.
- Benefits of Mutual Funds: They offer diversification, professional management, and liquidity. These funds are ideal for those who prefer a hands-off approach to investing but still want to benefit from the expertise of fund managers.
- Choosing the Right Mutual Fund: Factors such as fund performance, fees, and investment objectives should be considered when selecting a mutual fund. Understanding these elements can help you choose funds that align with your financial goals.
Derivatives: Complex but Useful
- Understanding Derivatives: Derivatives are contracts whose value is based on an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities. They are often used for hedging risks or speculating on asset price movements.
- Types of Derivatives: Common derivatives include options, futures, and swaps. Each type serves different purposes and comes with its own risk-reward profile, requiring a deep understanding before investing.
- Using Derivatives Wisely: While derivatives can enhance investment strategies by providing leverage or hedging against risks, they require careful risk management due to their complexity and potential for significant losses.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Flexibility and Cost-Effectiveness
- What Are ETFs?: ETFs are similar to mutual funds but trade on exchanges like individual stocks. They offer the benefits of diversification and flexibility, often at lower costs than mutual funds.
- Advantages of ETFs: They provide easy market access and liquidity, allowing investors to buy and sell throughout the trading day. ETFs often have lower expense ratios, making them a cost-effective option for building a diversified portfolio.
- Selecting the Right ETFs: When choosing ETFs, consider factors such as the underlying index, expense ratios, and trading volume. These elements can impact the fund’s performance and suitability for your investment goals.
Risk Management in Financial Instruments
Risk management is crucial when dealing with financial instruments. Each type of instrument carries its own level of risk. Stocks and derivatives are generally riskier than bonds and mutual funds. Understanding your risk tolerance is key to choosing the right instrument.
Assessing Risk Tolerance
- Understanding Personal Risk Tolerance: Risk tolerance varies from person to person, influenced by factors like age, financial situation, and investment goals. Assessing your willingness and ability to endure market fluctuations is crucial for choosing suitable investments.
- Tools for Measuring Risk Tolerance: Various tools and questionnaires are available to help investors gauge their risk tolerance. These tools provide insights into how much risk you can comfortably take on, guiding your investment decisions.
- Adjusting Risk Tolerance Over Time: As your financial situation and life circumstances change, your risk tolerance may evolve. Regularly reassessing your risk appetite ensures your investment strategy remains aligned with your current needs and goals.
Understanding Market Risks
- Types of Market Risks: Market risks can include interest rate risk, inflation risk, and economic downturns. Each type affects financial instruments differently, necessitating a comprehensive understanding to manage them effectively.
- Strategies for Mitigating Market Risks: Diversification, hedging, and the use of stop-loss orders are common strategies for reducing market risks. These techniques help protect your investments from adverse market conditions.
- The Role of Economic Indicators: Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation, can provide valuable insights into potential market risks. Monitoring these indicators helps you anticipate and respond to changes in the economic environment.
Building a Risk Management Plan
- Components of a Risk Management Plan: A robust risk management plan includes identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and implementing strategies to mitigate them. Regularly reviewing and updating the plan ensures its effectiveness.
- Incorporating Risk Management into Investment Strategy: Integrating risk management into your overall investment strategy helps maintain a balanced portfolio, aligning risk with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- The Importance of Flexibility in Risk Management: Financial markets are dynamic, requiring flexibility in risk management strategies. Being open to adjusting your approach in response to market changes is key to long-term investment success.
Steps to Choose the Right Financial Instrument
Choosing the right financial instrument is like crafting a compelling narrative; it requires a clear understanding and a step-by-step approach. Here’s how you can do it:
Step 1: Define Your Financial Goals
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term Goals: Clearly distinguishing between short-term and long-term financial goals is essential. Short-term goals might include saving for a vacation or an emergency fund, while long-term goals could be retirement savings or buying a house.
- Aligning Goals with Financial Instruments: Different financial instruments are better suited for different types of goals. For instance, safer options like bonds are ideal for short-term goals, while stocks and mutual funds may be more appropriate for long-term growth.
- Regularly Reviewing Goals: As life circumstances change, so too can financial goals. Regularly revisiting and adjusting your goals ensures that your investment strategy remains relevant and effective.
Step 2: Assess Your Risk Tolerance
- Identifying Your Comfort with Risk: Understanding your comfort level with risk involves recognizing how much market volatility you can endure without feeling anxious or making impulsive decisions.
- Tools for Gauging Risk Tolerance: Utilizing risk assessment tools and quizzes can provide a clearer picture of your risk tolerance, helping you make informed investment choices.
- Adapting to Changing Risk Profiles: Your risk tolerance may change over time due to factors like age, income, and financial goals. Being adaptable and willing to adjust your risk profile ensures that your investments remain in alignment with your life stage and circumstances.
Step 3: Research Asset Classes
- Understanding Different Asset Classes: Asset classes, such as equities, fixed income, and cash equivalents, have distinct characteristics and risks. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed investment choices.
- Analyzing Historical Performance: Examining the historical performance of various asset classes can provide insights into potential returns and risks, aiding in the selection of appropriate investments.
- Evaluating Current Market Conditions: Keeping an eye on current market trends and conditions helps you anticipate potential changes in asset class performance, allowing for timely adjustments to your investment strategy.
Step 4: Diversify Your Portfolio
- The Importance of Diversification: Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors. It helps mitigate the impact of poor performance in any single investment on your overall portfolio.
- Strategies for Effective Diversification: Effective diversification involves a mix of stocks, bonds, and possibly alternative investments like real estate or commodities. This approach balances risk and return, enhancing portfolio stability.
- Monitoring and Rebalancing Your Portfolio: Regular monitoring and rebalancing ensure that your portfolio remains diversified and aligned with your investment goals. This involves adjusting allocations as needed in response to market changes.
Step 5: Seek Professional Advice
- When to Seek Professional Help: If you’re uncertain about your investment decisions or lack the time to manage your portfolio, consulting a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and guidance.
- Choosing the Right Financial Advisor: Selecting a financial advisor involves considering factors such as their qualifications, experience, and fee structure. A good advisor tailors their advice to your unique financial situation and goals.
- Building a Collaborative Relationship: Working closely with your financial advisor as a partner in your financial journey ensures that their recommendations align with your values and objectives, leading to more effective investment decisions.
Practical Tips for Financial Success
Achieving financial success involves more than just selecting the right instruments; it requires ongoing management and strategic adjustments.
Stay Informed
- Keeping Up with Financial News: Regularly consuming financial news and staying updated on market trends helps you make informed decisions and anticipate potential changes in the economic landscape.
- Utilizing Financial Tools and Resources: There are numerous tools and resources available online, such as financial news websites, market analysis reports, and investment apps, to help you stay informed and engaged.
- Engaging with Financial Communities: Joining investment forums or communities allows you to learn from others, share insights, and stay motivated on your financial journey.
Review and Adjust
- Regular Portfolio Reviews: Conducting regular reviews of your portfolio ensures that your investments remain aligned with your goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
- Making Strategic Adjustments: Based on your reviews, making necessary adjustments to your investment strategy, such as rebalancing asset allocations or exploring new opportunities, helps you stay on track to meet your objectives.
- Learning from Mistakes: Embracing mistakes as learning opportunities allows you to refine your investment approach and make more informed decisions in the future.
Be Patient
- Understanding the Importance of Patience: Building wealth through investing takes time. Patience is essential for allowing your investments to grow and compound over the long term.
- Avoiding Impulsive Decisions: Avoiding impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations helps you maintain a consistent investment strategy and reduces the risk of emotional investing.
- Celebrating Milestones: Recognizing and celebrating your financial milestones, no matter how small, can provide motivation and reinforce positive investment habits.
Applying Financial Knowledge to Writing
Just like in writing, where structuring your plot and developing characters is key, structuring your investment strategy is vital for success. Here’s how you can apply these principles:
Structure Your Portfolio
- Creating a Balanced Portfolio: A well-structured portfolio, like a well-crafted story, requires balance and coherence. This involves diversifying investments and aligning them with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Revisiting and Revising Your Portfolio: Just as a writer revises drafts, revisiting and revising your portfolio ensures that it continues to meet your evolving needs and circumstances.
- Adapting to New Developments: Being open to adapting your portfolio in response to new developments, whether in the market or your personal life, ensures that it remains relevant and effective.
Develop Your Financial Character
- Knowing Your Investor Personality: Understanding your investor personality, whether cautious or adventurous, helps you make choices that align with your comfort level and financial objectives.
- Embracing Your Unique Financial Journey: Recognizing that your financial journey is unique allows you to focus on your own goals and progress, rather than comparing yourself to others.
- Building Confidence in Your Financial Decisions: Building confidence in your financial decisions, through education and experience, empowers you to take control of your financial future.
Craft Your Investment Dialogue
- Engaging with Your Investments: Actively engaging with your investments by staying informed and involved ensures that you remain proactive in managing your financial future.
- Communicating with Financial Advisors: Effectively communicating with your financial advisors helps ensure that their recommendations align with your goals and that you fully understand your investment strategy.
- Sharing Your Financial Insights: Sharing your financial insights and experiences with others, whether through discussions or writing, reinforces your knowledge and contributes to the broader financial community.
Conclusion
Choosing the right financial instrument doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By understanding your goals, assessing your risk tolerance, and diversifying your portfolio, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial narrative. Remember, every successful story—be it in writing or investing—begins with understanding and preparation. Happy investing!

